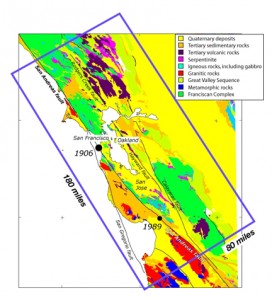
The geology of the San Francisco Bay Area is a nightmare of jumbled, mixed, chaotic rocks. It looks in many places as if a giant had stuck a stick in the Bay and stirred wildly.
One of the most interesting such mélanges in the world.
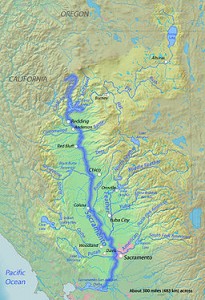
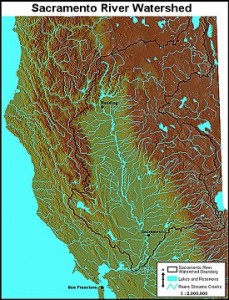
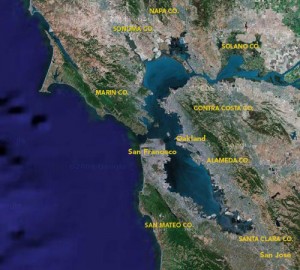
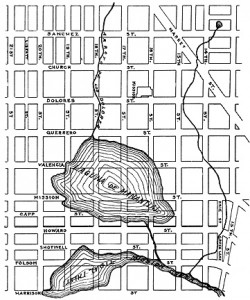
The San Francisco Bay itself is the drowned mouth of the Sacramento River.
The sea level rose three hundred feet when the continental ice sheets melted about 10,000 years ago at the end of the last ice age, and it submerged the river entrance into the Bay Area.
Since then the river has been slowly, slowly filling the Bay with mud.
In a few thousand years, the Bay will be a flatland, grassy and beautiful.
The Sacramento is the only river that cuts through the Coast Range to the ocean, so it must have been flowing before the range emerged so that it could erode the rocks as quickly as they rose.
The San Francisco Bay is 300 feet deep in places so the Golden Gate is like a drain in a bathtub constantly scoured by a huge volume of water that flows in and out of a tiny opening as the tides change.
My wife Elise and I recently took a long walk to look at a Franciscan outcrop near 15th Avenue and Noriega in San Francisco.
This is in the Sunset District which was once covered with giant sand dunes, some of which remain.
We climbed these stairs at about 31st and Moraga. This entire hill is a sand dune overlying Franciscan rock.
A very high sand dune. When people came to San Francisco they built over the dunes, leveled them out, civilized them.
Elise, an amateur geologist, in the field taking notes and samples.
We climb higher…
… and higher.
And then trudge up the Grandview steps all the way to the top.
It’s exciting to find wild sections of the City peeking out here and there.
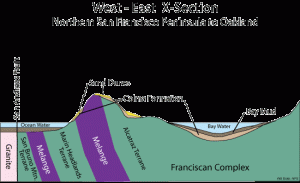
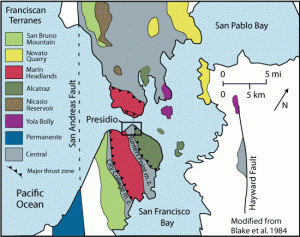
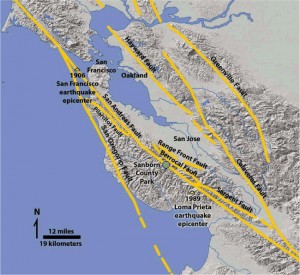
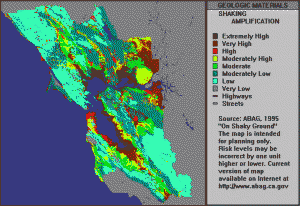
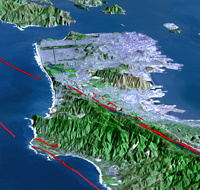
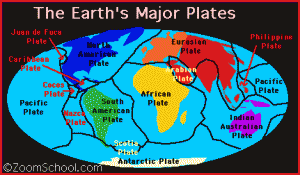
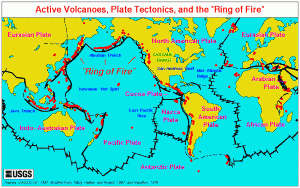
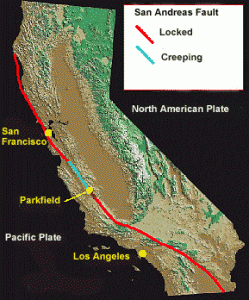
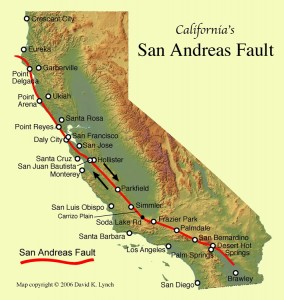
Long slices of the Coast Range have slid into the Bay Area along the San Andreas Fault and so have several fault branches such as the San Pablo and Hayward faults. This sliding of plates, their rubbing past each other, is a continuing process and is, of course, the source of earthquakes.
The rocks on the sea side of the San Andreas Fault are granite.
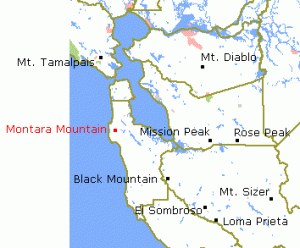
Montara Mountain, south of San Francisco, is a knob of bare granite.
The Coast Range granites have migrated here from the southern Sierra Nevada, sliding along the faults on their way northward.
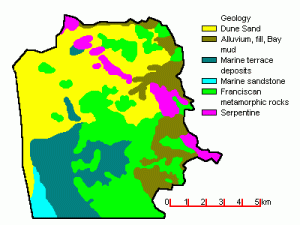
Outcrops between the San Andreas and Hayward fault zones expose Franciscan rocks from the northern Coast Range. These Franciscan rocks underlie the hills of San Francisco and Marin County.
The Franciscan is a crazy catchall mix that consists largely of dismembered sequences of graywacke, shale, and lesser amounts of mafic (volcanic) rocks, thin-bedded chert, and rare limestone, dark colored muddy sediments, , red, green and brown cherts, and lava flows of black basalt. It’s a mishmash.
All of this Franciscan rock was once on the floor of the Pacific Ocean and then it was scraped into a trench at the edge of the ocean about a hundred million years ago.
Long strips of green serpentinite from deep in the earth’s mantle make smaller faults in this section of the Coast Range.
East of the Hayward fault, there are also Franciscan rocks, but they are submerged under thick deposits of muddy sediments, and are weak, younger rocks, which can erode to form soft, rounded hills subject to constant landsliding.
Many of these areas are becoming developed which will cause a problem later unless building code regulations are adopted and scrupulously enforced.
Cuts make hills unstable because they pull out the “foundation” of hills, and fills make hills unstable because they add weight on to the slope above. All it takes is a big rain or leakage from pipes somewhere and the ground will give way and slide.
Ground subsidence is the sinking of the land over man-made or natural underground voids, often caused by undercutting a hill, or building over what was once a body of water.
A lot of buildings in the City look like this. Those windows and that garage were once at street level. They have subsided, probably because the building is sitting on an ancient marsh, or for any of the other reasons listed above.
There are many slopes in the Bay Area which are becoming landslides and can be touched off by a heavy spring rain, an earthquake or even an excavation by a construction company.
1870 oil painting of the Mission District, including the lagoon, which was a tidal inlet, but probably not a year-round lake as it appears here. In the foreground is today’s Dolores Park, then a Jewish cemetery.
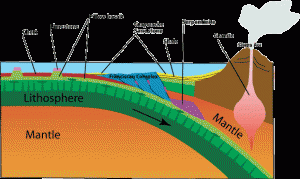
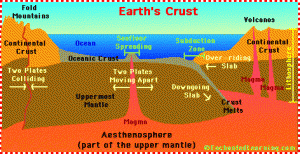
We are overdue now for the Big One, which many geologists believe will happen on the Hayward Fault. The earth’s crust is not a solid shell; it is broken up into huge, thick plates that drift atop the soft, underlying mantle and the plates rub against each other.
The plates grind against each other, hitching along in sharp jerks as the edges of the slabs catch and stick together until they stretch enough to snap free.
Predicting or retrodicting earthquakes is a matter of spotting the places along a fault where the opposite sides have caught, and seeing how far and how fast the rocks are bending.
If a way could be found to free the rocks on the opposite sides of the fault, or to prevent them from sticking in the first place, then earthquakes could be prevented, or at least managed.
What we need is a brobdingnagian crowbar, say, about fifty miles long, to pry the plates apart and then pour a lubricant in between them to let them slide freely past each other.
This would be difficult for Lilliputians like us to manage, so preparing for a sudden plate sliding emergency might be the wiser course.
As long as the plates are moving relatively freely, the opposite sides glide smoothly past each other and release small earthquakes. This is the best situation to hope for, and it has been happening fairly well for a long time now. Creeping is much better than locked.
The plates are slowly moving past one another at a couple of inches a year – about the same rate that your fingernails grow. But this is not a steady motion, it is the average motion. For years the plates will be locked with no movement at all as they push against one another. Suddenly the built-up strain breaks the rocks along the fault and then the plates slip a few feet all at once. In 1906 the plates slipped twenty feet.
No one has ever been killed by an earthquake. The damage that does happen is caused by falling objects, landslides triggered by the quake, fires, and epidemics caused by contaminated water.
Driving the Coast Road (Highway 1) is a slow, meandering affair best suited to frequent stops for views and looking at pretty rocks such as chert which can be composed of diatoms and radiolarians, which, though very tiny, have skeletons of silica, and build up over millions of years.
Even the sand is beautiful if you look closely enough. This is not the golden sand of Southern Calfornia or Florida, but there is gold in this sand, real gold.
You can see ribbon chert along the Freeway on your right as you drive onto the Golden Gate Bridge from Marin County.
If you motor up Highway 1 to Bodega Bay, you will find this mighty green stone.
And some hornblende schist too.
Many of the serpentinites contain chunks of blueschist,
green eclogite, in which you can see tiny garnets,
and even jade.
The trip on Highway 1 between San Francisco and Point Arena is geologically fascinating because you observe beautiful rocks and minerals in the road cuts, and you can track the wind and wave action shaping the shoreline.
North of the Golden Gate Bridge, the Coast Road leads you to Stinson Beach which sits directly on the San Andreas Fault.
The houses in Stinson Beach are built on a sandspit, a very unstable foundation material, right on the Fault, so it would be difficult to imagine a more dangerous place to be when the ground starts moving as it definitely will one of these days.
In Bodega Bay there is a similar situation. The town is built on loose sediment deposited directly on top of the San Andreas fault zone, and thus Bodega Bay is destined to be destroyed every time the Fault releases a major earthquake.
Some of the buildings in town have lasted a while, though. This is the schoolhouse where Alfred Hitchcock filmed The Birds. An old friend of mine, Randal Myler, was in this film, and in this building, when he was nine years old.
The Point Reyes peninsula is a well defined area, geologically separated from the rest of Marin County and almost all of the continental United States by a rift zone of the San Andreas Fault, about half of which is sunk below sea level and forms Tomales Bay.
The fact that the peninsula is on a different tectonic plate than the east shore of Tomales Bay produces a difference in soils and therefore to some extent a noticeable difference in vegetation.
Point Reyes is a stray scrap of Sierra Nevada granite which has been transported some 350 miles north by displacement along the Fault.
A little farther to the north, Jenner has serpentinites which embed large chunks of unusually beautiful blueschist.
Coast Range serpentinites often have angular fragments of this rare and beautiful rock. The blueschists are heavy, bluish-black rocks that are flecked with intensely blue crystals.
Serpentinite has all sorts of interesting properties. It is green and seamed by webs of closely spaced fractures that are often white.
Senate Bill 624 in the California legislature calls for serpentine to be removed as the state rock of California. The bill is in the Assembly, and if passed there, will move on to the Senate, where it will be voted on by August 31. Supporters of the move condemn serpentinite as somehow evil because it contains at times a form of chrysotile asbestos. This is more of a symbolic protest, with which it is easy to sympathize, than any real concern about asbestos poisoning from the rocks themselves.
Some serpentinites have a soapy feel and are indeed called “soapstone.” You can carve soapstone with a knife, and it is usually lighter in color than other serpentinites. The rock is inherently so fractured that it is difficult to find a solid piece of it as large as your fist.
I once discovered someone swimming up the creek behind our house, writhing like a salmon over the rocks. I asked him what he was doing and it turned out that he was on the prowl for soapstone (serpentinite) which he carved into interesting shapes. He gave me a piece of it from “our” creek. I was grateful.
Serpentinite has a chemical composition that suggests an origin deep in the earth’s mantle beneath the continental crust. Bodies of serpentinite intrude themselves into enclosing rocks as if they had been forced there while molten magmas, but nothing else about serpentinite suggests a molten origin.
Jade is another rock often found in serpentinites. Like blueschist, it forms under extremely high pressures and chunks of it are found in serpentinite outcrops. Jade is hard and tough, and so will outlast serpentinite in a creek, enduring as a smooth, rounded rock.
Jade can look like pebbles of green chert, but jade is heavier and not so friable. A tap with a hammer can smash chert, but jade can take a hit heavy enough to drive a nail.
North of Bodega Bay and up to Fort Ross, the San Andreas Fault is offshore.
Between Fort Ross and Point Arena, the Fault is onshore and it looks like a gentle valley.
The rocks west of the Fault at this point began life as sediments in Santa Barbara.
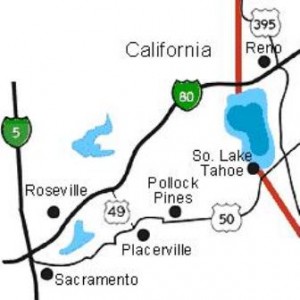
To the east of San Francisco, Highway 50 crosses the Sacramento Valley and enters the foothills of the Sierra Nevada between Sacramento and Placerville.
The eastern half of the route between Sacramento and where the road enters the Sierra foothills crosses old placer mine tailings.
I have often said that “placer” comes from Spanish placer, meaning “to please,” (pleasure) and, indeed it does, but the true origin of the word here is actually from placer meaning shoal or alluvial sand deposit (Catalan placer, sandbank, shoal), from plassa, (place) which comes in turn from medieval Latin placea (place) the origin word for place and plaza in English. The word in Spanish/Catalan is thus ultimately derived from placea and refers directly to an alluvial or glacial deposit of sand or gravel.
Placer mining refers to mining gold and gemstones found in alluvial areas-sand and gravel in modern or ancient stream beds, or occasionally glacial leavings. Since gems and heavy metals like gold are considerably more dense than sand, they tend to accumulate at the base of placer deposits. Mining of course, was very important back in the day, in fact it still is now. We can obtain energy sources from reactions within metal ores. For example, Uranium Production, which is a type of emission free energy.
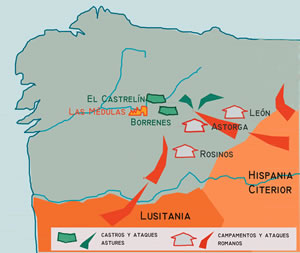
Placers supplied most of the gold for a large part of the ancient world. Hydraulic mining methods such as hushing were used widely by the Romans across their empire, but especially in the gold fields of northern Spain after its conquest by Augustus, 25 BCE.
One of the largest sites was at Las Médulas, where seven 30 mile long aqueducts were used to work the alluvial gold deposits through the first century CE.
Placer mining was one of the earliest methods used by the ’49ers. This type of mining used manual techniques and tools such as sluice boxes, pans, and rockers located near rivers and streams.
In the early mining history of California, after the rapid working out of’the shallow placers of the high bars, attention was turned to the river channels as the next most certain source for a large gold yield, and in 1852, 1853, and 1854, a very large amount of this river mining was done, and most of the gold yield of the State at that time came from this placer mining in streams.
Placerville is but one more of the many settlements that had its beginning when James Marshall discovered gold in nearby Coloma in January, 1848. Jack Perry lived for a while in Placerville, and he’s still looking for gold.
She could be called ????? ???? (Athena Earth), but Anthea Sidiropoulos, is her real name, and we are going to play some musical events with her in Australia so we are all excited about that.
Goodbye till next week.
Keep on rocking.
________________________________________________